Imagine a team member who never gets tired, immediately learns new tasks, and always follows the applicable rules and processes. What sounds utopian is becoming tangible reality through AI agents for businesses. But beyond the hype, many decision-makers face the same questions: What exactly is an AI agent? How does it differ from a simple chatbot? And how can you integrate this technology securely and profitably into existing business processes?
Table of Contents
What are AI Agents – and what distinguishes them from chatbots?
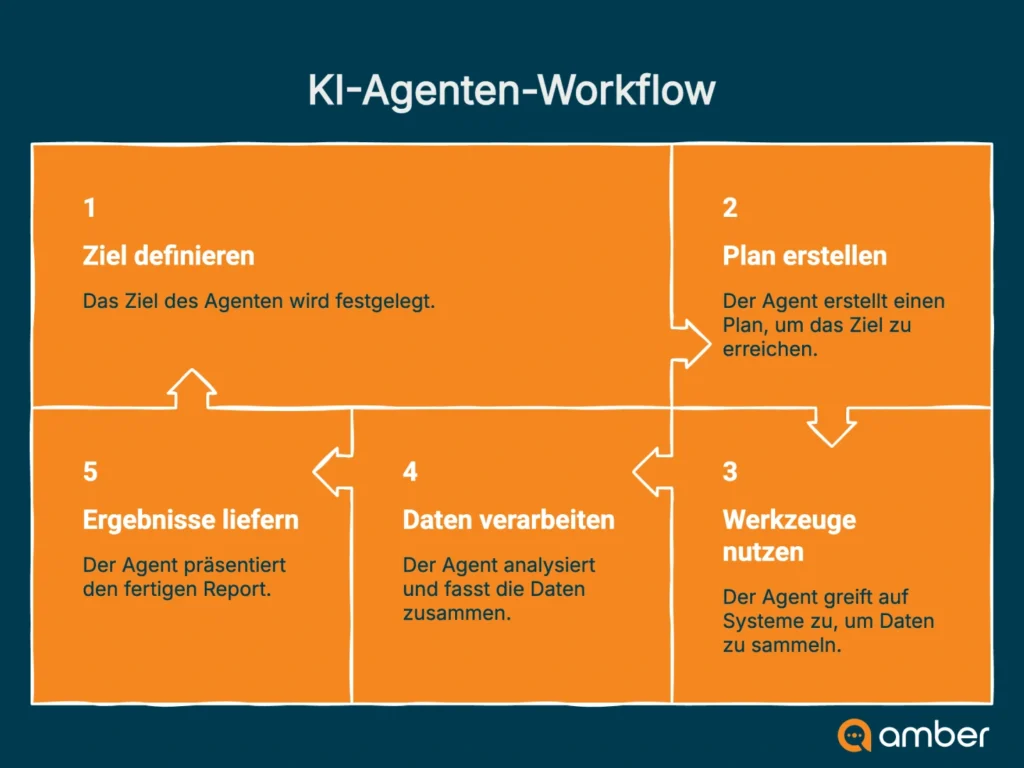
An AI agent pursues a clear goal (e.g., “Prepare a project report for the last quarter”), plans multiple sub-steps, uses tools/data sources, and checks intermediate results.
A chatbot primarily answers individual questions – an agent delivers results.
Agent vs. Chatbot (Quick Comparison)
| Criterion | Chatbot | AI Agent |
| Goal Orientation | Question → Answer | Goal → Plan → Execution → Result |
| Tool Access | limited | broad (APIs, files, systems) |
| Data Basis | often static | live & connectable |
| Governance | often unclear | role/rights-based, logged |
| Result Quality | varies | validated, repeatable |
Imagine you ask your new digital colleague to create the quarterly closing report. Depending on the configuration, they react as follows:
- Thinking and Planning: The agent breaks down the goal into logical steps: “First, I need the sales figures from the CRM, then the project updates from Jira, and finally the budget overview from the finance software.”
- Using Tools (Tool-Use): They independently access the various systems, as if logging in with their own account. They strictly observe the permissions assigned to them.
- Processing Information: They extract the relevant data, summarize it, and recognize connections – for example, that a budget surplus in project “Alpha” is due to postponed milestones.
- Delivering Results: In the end, they present you with a finished report draft, including a summary of the most important findings and the sources on which their analysis is based.
The crucial difference lies in autonomy and goal orientation. While a chatbot responds to an input with a single output, an AI agent plans and executes a chain of actions to achieve a complex goal. It is not a pure question-answer system, but a proactive, digital employee.
Use Cases that Create Immediate Value: Stories from Practice
The true strength of AI agents for enterprises is not shown in theory, but in daily practice. Let’s dive into three concrete scenarios that may sound familiar to you.
The Hunt for the Right Information: How the R&D Department Got Their “Treasure Map”

In the research and development department of an automotive supplier, there was a familiar problem: valuable knowledge was scattered across dozens of network drives, SharePoint sites, and old Confluence instances. An experienced engineer, shortly before retirement, was often the last resort because he could still remember “that one document from 2015.”
The AI Agent as Knowledge Archaeologist: Instead of starting a weeks-long manual search, an AI was tasked with a clear goal: “Find all relevant documents on material fatigue in polymer composites and summarize the most important findings.” The agent independently searched all connected systems, analyzed hundreds of documents – from old PDFs to current test reports – and created a clear summary within minutes. It even marked contradictory statements and identified knowledge gaps. The team not only saved days of research time but also rediscovered long-forgotten knowledge.

Result: Reduction of research time by 80% and avoidance of expensive duplicate developments.
The Overloaded Inside Sales Department: How Quotes Became Timely Again
In the inside sales department of a medium-sized mechanical engineering company, requests for standard spare parts were piling up. Each cost estimate was a manual process: check availability in the ERP, search for customer-specific discounts in the CRM, clarify delivery times, and laboriously copy everything into a quote template. Valuable time was lost, during which the sales colleagues could actually have been proactively advising customers.
The AI Agent as Quote Assistant: An agent was trained to take over this process. When inside sales now receives a request, they forward it to the agent. The agent independently checks all systems, calculates the price correctly, and creates a finished quote draft in corporate design. The employee only needs to briefly review and send the document.
Result: Quote creation for standard parts now takes only 2 minutes instead of 25 minutes. The team has more time for complex projects again, and customer satisfaction increases through fast response times.
The Compliance Puzzle: How the Legal Department Took the Terror Out of Audits
For the compliance department of a financial services provider, every internal audit was a nightmare. Hundreds of emails, contracts, and process descriptions had to be manually reviewed to prove compliance with a new regulation. The search was error-prone and tied up the entire department’s capacity for weeks.
The AI Agent as Audit Support: The agent received the task: “Collect all evidence for the implementation of the new XY directive from the last year.” The agent searched through the document management system (DMS), email archives, and contract management. It created complete, auditable documentation including references to the exact locations.
Result: Preparation time for the audit was reduced from three weeks to two days. The evidence documentation was complete and error-free.
These examples show only a fraction of the possibilities. Here you can dive into 10 proven use cases for AI agents in sales, service, HR and more.
How AI Agents are Securely Integrated into Your IT Landscape: Architecture and Interfaces
An AI agent is only a valuable relief if it fits seamlessly and securely into your existing IT infrastructure. At amber, we have designed the architecture of our AI agents for enterprises from the ground up to not only take the concerns of IT managers seriously but to proactively address them. The core principles are control, security, and openness.

No Loss of Control: Your Data, Your Rules
Perhaps the biggest concern when introducing AI is the potential loss of control over company data. Our architecture ensures that you remain in control at all times:
- Respect for Permissions: An AI agent never acts in a vacuum. It logs into your systems (e.g., Microsoft 365, Confluence, Jira) with its own identity or uses that of the respective user via Single Sign-On (SSO). This means: The agent sees and is allowed only what a human colleague with the same rights would see and be allowed to do. No new “super users” are created that can access everything uncontrollably.
- Traceable Actions: Every action an agent performs – every search, every data export, every write operation – is logged without gaps. This creates auditable transparency that is essential for compliance and troubleshooting.
- Flexible Operating Models: With good providers, you decide where your data is processed. Whether in the secure EU cloud, in your own private cloud, or completely on-premises in your data center – the ideal architecture adapts to your security requirements, not the other way around.
Seamless Connection: Open to Your System Landscape
An AI agent only unfolds its full benefit when it can access the relevant data sources and tools. That’s why we rely on an open and extensible integration concept.
| Integration Type | Examples | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Connectors | Microsoft 365, SharePoint, Teams, Confluence, Jira, Slack | Fast connection of the most important collaboration and knowledge platforms. |
| Databases & File Systems | SQL databases, network drives (SMB/NFS), DMS | Access to structured data and unstructured document repositories. |
| Business Systems (via API) | SAP, Salesforce, DATEV, Personio | Integration into core processes such as sales, finance, and HR. |
| Individual Connections | Proprietary in-house applications | Your specific legacy systems can also be connected via a flexible API interface. |
The integration is not a one-time, rigid process. Simply start with a single data source, such as the Confluence wiki, and gradually connect additional systems once the agent’s benefit has been proven.
Here you can learn in detail which systems amber supports by default and how we realize individual integrations.
What Do You Need to Consider for a Legally Compliant AI Agent in Your Enterprise?
Security, GDPR & EU AI Act: What Companies Really Need to Check Now
As soon as AIs process company knowledge, one topic automatically moves to the center: compliance. For legal, data protection, and IT security departments, it’s not crucial how “smart” a system is – but whether it is controllable, auditable, and cleanly fits into existing governance. Anyone who wants to introduce an AI agent should therefore systematically pay attention to the following areas:
1. Data Protection by Design & GDPR Compliance
A compliant AI agent addresses the following data protection questions:
- Purpose limitation & data minimization must be technically enforced, not just organizationally regulated.
- Data subject rights (information, deletion, restriction) must remain enforceable even in AI-supported processes.
- Data sovereignty is central: Where do models run, where are indexes located, where are logs stored? Hosting in the EU – ideally in Germany – makes classification considerably easier.
This becomes practically relevant as soon as AI systems are to access shared network drives, M365, or ticketing systems – precisely the systems that are typical in local corporate IT.
2. No Unwanted Model Training
One of the biggest compliance risks arises when company data flows uncontrollably into global models. Companies should therefore explicitly check:
- Are contents used exclusively for inference, not for training?
- Is it contractually and technically excluded that data is passed on to third parties or incorporated into public model pools?
- Are there clear scopes defining which data an agent may use and which not?
An IT infrastructure that prioritizes clear governance and stable systems should look very closely here.
3. Certified Security Processes
Many companies today orient themselves to established standards such as ISO 27001 to assess risks. For AI agents, this means:
- Access controls are documented and testable.
- Security incidents are treated procedurally, not ad hoc.
- Logs are complete, tamper-proof, and audit-capable.
These standards are not “nice to have” but the basis for deploying solutions in heavily regulated environments (e.g., manufacturing, engineering, service).
4. EU AI Act: Preparation for Coming Obligations
The EU AI Act defines clear requirements for the first time based on the risk of an AI system. For companies, this means:
- Documentation & Transparency: What data does the agent use, what risks exist, how is it controlled?
- Human-in-the-Loop: Where must humans be able to review or approve decisions?
- Technical Logging: Every model interaction must be auditable.
Anyone who relies on AI today should prefer systems that are not just “retrofitting” these requirements but are already designed for them, so compliance doesn’t become an innovation brake.
Interim Conclusion on Compliance – Long Story Short
An AI agent is only enterprise-ready if it is transparent, controllable, and integrable into existing security and data protection structures.
Specifically, this means:
- no black-box mechanisms
- clear, verifiable data flows
- complete logging
- technical & organizational measures at EU standard
- clear governance for model access and authorization
This doesn’t create “AI for AI’s sake” but a tool that convinces legal, data protection, and IT teams just as much as the specialist departments.
Here you can dive deep into our comprehensive security and data protection measures and view all relevant certificates.
Your Implementation Roadmap: From Pilot Project to Enterprise-wide Success in 5 Phases
The introduction of AI agents is not a purely technical change but a strategic transformation. A well-thought-out plan is the key to minimizing risks, achieving quick successes, and securing acceptance throughout the entire company. The following 5-phase model has proven to be an effective way for us in practice to get you from the first concept to scaled operation:
Phase 1: Goal Formulation (Week 1-2)
What happens? We start with a joint workshop to understand your current situation. What problem should be solved? Which use case promises the greatest and fastest benefit? We define a clear, measurable goal for an initial pilot project. Example: “Processing time for standard service requests should be reduced by 30%.”
Your contribution: You bring the right people to the table: a representative from the specialist department who knows the pain point, and a contact person from IT.
Phase 2: Build Test Pilot (Week 3-6)
What happens? We set up the first AI agent in a secure test environment. We connect the first, most important data source (e.g., your Confluence wiki) and train the agent on the selected use case. A small group of test users provides initial, valuable feedback.
Your contribution: You provide test data and enable testers to actively contribute.
Phase 3: The Dress Rehearsal (Week 7-10)
What happens? The pilot agent is tested under real conditions. We measure performance based on the goals defined at the beginning. Does everything work as expected? Where is there still room for optimization? This is the crucial phase to prove practical suitability.
Your contribution: Your test users work with the agent and document their experiences. Honest feedback is worth gold here.
Phase 4: The Launch Party (Week 11-12)
What happens? We evaluate the pilot’s results together. Has the goal been achieved? Then the agent goes live! We train future users and communicate the success in the company. This first “quick win” is the best advertisement for further scaling.
Your contribution: You celebrate the success with the team and plan the next steps.
Phase 5: Scaling and Operation (continuous)
What happens? After the first success, it’s time to realize the next “quick wins.” We identify additional use cases, connect additional data sources, and gradually roll out the AI agents in other departments. A central governance model ensures that you don’t lose track.
Your contribution: You establish an internal competence team that drives scaling and serves as a central contact for users.
This structured approach takes the complexity out of introducing AI and makes it a manageable, iterative process. You don’t have to do everything at once. Start small, learn quickly, and build on your successes.
Here you’ll find our detailed 5-phase practical guide for implementing AI agents – including checklists and best practices.
ROI & Measurement: What AI Agents are Really Worth for Your Enterprise
In the end, every business decision comes down to one question: What’s in it for us? Investment in artificial intelligence is no exception. However, the return on investment (ROI) of AI projects cannot always be measured only in euros and cents. It is composed of hard, quantitative metrics and softer but no less important qualitative factors.
The Hard Facts: Time is Money
The most direct and easiest to measure benefit of AI agents lies in efficiency gains. Consider the example of our inside sales department, which previously needed 25 minutes for a standard quote. With the AI agent, it’s only 2 minutes. That’s a time saving of 23 minutes per quote.
Let’s calculate this:
Assumptions:
- 20 quotes per day
- 23 minutes time saving per quote
- Internal hourly rate of €50
Calculation:
- Daily time saving: 20 quotes × 23 minutes = 460 minutes ≈ 7.7 hours
- Monthly time saving (at 20 working days): 7.7 hours/day × 20 days = 154 hours
- Monetary benefit: 154 hours × €50/hour = €7,700 per month
This value alone often justifies the investment. But that’s just the tip of the iceberg.
The Soft Factors: Priceless, but Decisive
In addition to direct cost savings, there are a number of advantages that may not immediately show up in the balance sheet but significantly influence long-term business success:
- Employee Satisfaction: Who likes to do dull, repetitive tasks? By having AI agents take over these activities, your employees can concentrate on what really counts: creative problem-solving, strategic planning, and direct customer contact. This not only increases motivation but also makes you more attractive as an employer.
- Decision Quality: AI agents can analyze huge amounts of data in the shortest time and uncover connections that would have remained hidden from a human. This leads to more informed, data-driven decisions in all business areas.
- Error Reduction: Manual processes are error-prone. A transposed number here, a forgotten email there… Small errors can have big impacts. AI agents work with constant precision and drastically reduce the risk of human oversights.
- Knowledge Democratization: Valuable expert knowledge that today is often trapped in the heads of individual employees is made accessible to the entire company through AI agents. This reduces dependencies and secures your company knowledge in the long term.
The true value of AI agents lies in the combination of these factors. They are not just a tool for cost reduction but a strategic lever with which you make your company more agile, more intelligent, and more future-proof.
Your Next Step: Make the First Move
You have now seen that AI agents are strategic tools with which you make your company more knowledge-based, more agile, and more future-proof. The path from theory to practice is shorter than you might think.
Are you ready to see how an AI agent works with your own data and in your own system environment? Request your personal demo now. We’ll show you in a 30-minute conversation how we identify an initial use case in your company and bring it to life together with a risk-free pilot.
Request Your Personal Demo Now
FAQs: The Most Common Questions About AI Agents in Enterprises
1. What distinguishes amber’s AI agents from other tools?
While generic assistants like ChatGPT are powerful tools for general tasks, our amberAgents are specifically designed for use in enterprises. The crucial difference lies in the secure and deep integration into your existing system landscape. Our agents work exclusively based on your internal, verified data sources and 100% respect your permission structures. They are a transparent, controllable, and data protection-compliant part of your corporate IT.
2. How do you ensure that an agent only sees the data it’s allowed to see?
An amberAgent never acts outside the permissions you give it. Access to your systems (e.g., Microsoft 365, network drives) always occurs via an identity that is subject to the same rules as any human employee. If an employee from the marketing department has no access to financial data, an agent working for them doesn’t have this access either. This is ensured via your existing identity management (e.g., via SSO/Entra ID).
3. Can AI agents also change data in our systems?
Yes, but only if you explicitly allow it. You have full control. Via policies, you can precisely define which actions an agent may perform. For example, you can specify that an agent in the service area may only “create draft responses” but never finally close a ticket. This way, you can start with read access and gradually enable more write capabilities as trust in the process grows.
4. How do you avoid “hallucinations,” i.e., the invention of facts?
Our agents are trained to work source-guided. This means they don’t invent answers but always derive them from the verified data sources you’ve connected. For every statement an agent makes, it provides the exact evidence on request – the link to the document, the page, and the paragraph on which its information is based. This makes its results verifiable and creates trust.
5. Does this also work with our old, self-developed systems?
In most cases, yes. In addition to a broad range of standard connectors for common business applications, we have a flexible API interface. Through this, we can also connect older “legacy” systems, databases, or individual in-house solutions, as long as programmatic access is possible.
6. How do we best get started without overwhelming ourselves?
The best way is a clearly focused pilot project. Don’t choose the biggest, most complex problem, but a use case with a clear pain point and measurable benefit (a “quick win”). Our 5-phase model is designed precisely to guide you safely and step-by-step from this first pilot to enterprise-wide success. Focus on one goal, one specialist department, and one data source – and build on that.
